Welcome, digital explorers, to the age of AI assistants-where your words are the magic spells that conjure up everything from poems to Python code, marketing strategies to meal plans. But here’s the rub: the quality of what you get from an AI is only as good as the prompt you give it. Think of prompt engineering as the art of asking the right questions, in the right way, to get the answers you actually want. Whether you’re a content creator, marketer, developer, or just someone who likes having robots do their bidding, mastering prompt writing is the secret to unlocking AI’s full potential.
Let’s break down the essential principles of prompt engineering, sprinkle in real-world examples, and arm you with techniques that’ll make your prompts (and your AI outputs) the envy of the digital realm.
What is a prompt (and why should you care)?
A prompt is simply the instruction or input you give to an AI assistant-your way of telling it what you want. But don’t be fooled by the simplicity: a vague prompt leads to generic, often disappointing results, while a well-crafted prompt can yield responses that are insightful, creative, and spot-on for your needs.
Why does this matter? Because AI assistants are not mind readers. They interpret your instructions literally, so the clearer and more detailed you are, the better the output. In the world of SEO, marketing, and content creation, this can mean the difference between page-one glory and digital obscurity.
Clarity and specificity: Your new best friends
Let’s start with the golden rule: be clear and specific. Imagine asking a friend, “Tell me about dogs.” You might get a rambling monologue about everything from poodles to police K9s. Now try, “Write a 200-word blog post about why Labradors make great family pets, using a friendly tone.” Suddenly, you’re getting exactly what you need.
Vague Prompt:
Write a story.Specific Prompt:
Write a short science fiction story set on Mars about a robot discovering an ancient artefact.The difference is night and day. The second prompt gives the AI a clear genre, setting, character, and plot hook, resulting in a much more tailored response.
The power of context
Context is the secret sauce that helps AI assistants understand why you’re asking for something and who it’s for. The more background you provide, the smarter and more relevant the AI’s response will be.
Without Context:
Generate blog ideas.With Context:
Generate five SEO-friendly blog topic ideas to publish the results of an in-depth case study targeting small businesses focused on machine learning.Notice how the second prompt includes the audience, subject, and purpose, leading to much more actionable output.
Defining the desired output format
Don’t leave the format to chance. If you need a list, a table, a poem, or code in a specific language, say so. This helps the AI structure its response and saves you from unnecessary editing.
Examples:
- Summarise the article in five bullet points.
- Provide the information in a Markdown table.
- Write a Python script that sorts a list of numbers.
Using keywords effectively (for AI and SEO)
Keywords aren’t just for Google-they can help guide the AI, too. When you embed relevant keywords in your prompt, you steer the AI towards the topics and terminology that matter most. This is especially crucial for SEO content, where aligning with search intent can boost your rankings.
Prompt for AI:
Generate a list of SEO keywords for an educational article about social media influencer software.Prompt for SEO:
Generate a comprehensive list of long-tail keywords for architectural services that reflect a local commercial search intent by high-income households.The difference? The latter is laser-focused on both the topic and the searcher’s intent, making it more valuable for SEO.
Specifying tone and style
AI can write like Shakespeare or your favourite TikTok influencer-if you tell it how. Always specify the tone and style you want, especially for brand consistency or audience engagement.
Examples:
- Write in a formal, academic tone.
- Adopt a witty, conversational style.
- Use a persuasive and professional voice suitable for a B2B audience.
Iteration and refinement: The art of getting it right
Don’t expect perfection on the first try. The best results often come from tweaking your prompts based on the AI’s initial responses. Ask it to elaborate, simplify, or focus on a different aspect. Iterative refinement is your friend-think of it as having a dialogue with the AI, not a one-off transaction.
Example:
- Initial prompt: Write a product description for a smartwatch.
- Refined prompt: Write a 100-word product description for a smartwatch, highlighting its fitness tracking features and targeting tech-savvy millennials. Use an enthusiastic, energetic tone.
Utilising different prompting techniques
Ready to level up? Here are some advanced techniques to supercharge your prompts:
- Role-playing:
Act as a cybersecurity expert and explain the risks of public Wi-Fi to a non-technical audience. - Chain-of-thought prompting:
Explain step-by-step how a bill becomes law in the UK, starting from proposal to royal assent. - Few-shot prompting:
Here are two examples of good product reviews. Now write a third one for this new product: [product details]. - Negative constraints:
Write a summary of the article, but do not mention the author’s name or publication date.
These strategies help you shape the AI’s output to match your needs, whether you’re after creative writing, technical documentation, or anything in between.
Negative prompt example
This demonstration shows how negative prompting can be used on algorithmically-generated artworks created using the Stable Diffusion V1-4 AI diffusion model. Negative prompts instruct the AI to omit certain objects, motifs, or visual elements when generating an image, unlike positive prompts which instruct it to include them.
This image illustrates the process of using negative prompting within Stable Diffusion to fine-tune the output of an AI-generated image based on user desires, as part of a three-image series showing each step of the procedure.
Prompt: Hakurei Shrine in distance, Gensokyo, nature landscape, landscape art, far view from distance, traditional Japanese architecture in distance, Shinto shrine in distance, forests, mountains, rivers, art style of Craig Mullins and Jordan Grimmer and Tyler Edlin and Darek Zabrocki and Raphael Lacoste.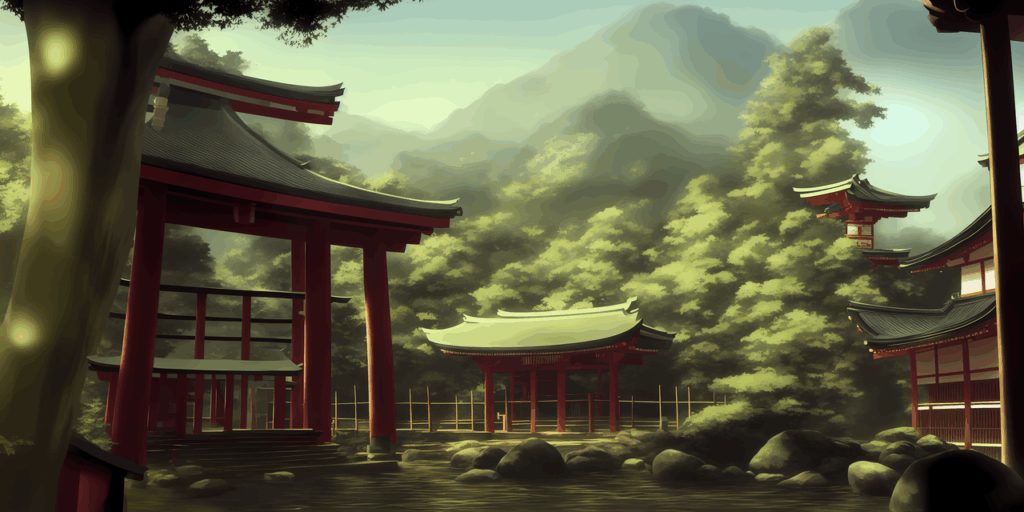
Using exactly the same seed and positive prompt, two more pictures were generated. This time, however, negative prompts were used.
Prompt: Hakurei Shrine in distance, Gensokyo, nature landscape, landscape art, far view from distance, traditional Japanese architecture in distance, Shinto shrine in distance, forests, mountains, rivers, art style of Craig Mullins and Jordan Grimmer and Tyler Edlin and Darek Zabrocki and Raphael Lacoste.
Negative prompt: Green trees.
Prompt: Hakurei Shrine in distance, Gensokyo, nature landscape, landscape art, far view from distance, traditional Japanese architecture in distance, Shinto shrine in distance, forests, mountains, rivers, art style of Craig Mullins and Jordan Grimmer and Tyler Edlin and Darek Zabrocki and Raphael Lacoste.
Negative prompt: Round stones, round rocks.
Understanding negative prompts in the context of artificial intelligence is crucial for optimising model performance and ensuring accurate outputs. They serve as examples of how specific wording can lead to undesired responses or misinterpretations by AI assistants. By recognising these pitfalls, we can refine our prompt engineering techniques, ensuring clarity and precision when interacting with AI models. This awareness not only improves the quality of AI-generated content but also contributes to more efficient and effective use of AI in various professional applications.
Handling ambiguity and eliciting clarification
AI can get confused by ambiguous prompts-just like humans. If you suspect your prompt isn’t clear, ask the AI to request clarification.
Example:
If anything in my prompt is unclear, ask me follow-up questions before answering.This not only improves the quality of the output but also helps you refine your prompt-writing skills over time.
Ethical considerations and responsible prompting
With great power comes great responsibility. Avoid prompts that could generate harmful, biased, or unethical content. Always review AI outputs for accuracy and appropriateness, especially when dealing with sensitive topics or public-facing content.
Tools and resources for better prompt writing
- Prompt libraries: Online repositories like PromptBase or GitHub collections for inspiration.
- SEO tools: Platforms like Clearscope, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to identify relevant keywords and search intent.
- AI communities: Subreddits like r/ChatGPTPromptGenius for real-world examples and peer feedback.
- Templates: Develop your own prompt templates for recurring tasks, saving time and ensuring consistency.
Real-world examples and case studies
Let’s see prompt engineering in action across different domains:
Writing:
Write a 500-word blog post about the health benefits of green tea, targeting health-conscious adults in the UK. Use a friendly, informative tone and include recent scientific studies.Coding:
Generate a Python function that takes a list of numbers and returns the median. Include comments explaining each step.Research:
Summarise the key findings of the latest IPCC climate report in three bullet points, suitable for a general audience.Creative tasks:
Write a limerick about a cat who loves to travel by train.Case studies consistently show that prompts with clear instructions, context, and constraints yield more accurate, actionable, and SEO-friendly outputs.
Final thoughts: Your prompt, your power
Mastering prompt engineering is like learning to wield a new superpower. The more you practise, the more you’ll discover just how much you can achieve with the right words in the right order. Whether you’re aiming for Google’s front page, coding efficiency, or creative brilliance, the key is clarity, context, and a willingness to iterate.
So, next time you fire up your favourite AI assistant, remember: the future belongs to those who ask better questions.
Curious about a specific use case or want to see more prompt examples? Drop your scenario below and let’s engineer some AI magic together!



